
Putting an incident response plan into action is an example of an administrative corrective control. Examples of technical corrective controls include patching a system, quarantining a virus, terminating a process, or rebooting a system. Honeypots and IDSs are examples of technical detective controls.Ĭorrective controls include any measures taken to repair damage or restore resources and capabilities to their prior state following an unauthorized or unwanted activity. Physical examples include alarms or notifications from physical sensor (door alarms, fire alarms) that alert guards, police, or system administrators. Examples include physical controls such as fences, locks, and alarm systems technical controls such as antivirus software, firewalls, and IPSs and administrative controls like separation of duties, data classification, and auditing.ĭetective controls describe any security measure taken or solution that’s implemented to detect and alert to unwanted or unauthorized activity in progress or after it has occurred. Preventative controls describe any security measure that’s designed to stop unwanted or unauthorized activity from occurring. Security awareness training for employees also falls under the umbrella of administrative controls.

These can apply to employee hiring and termination, equipment and Internet usage, physical access to facilities, separation of duties, data classification, and auditing. Some common examples are authentication solutions, firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection systems (IDSs), intrusion protection systems (IPSs), constrained interfaces, as well as access control lists (ACLs) and encryption measures.Īdministrative controls refer to policies, procedures, or guidelines that define personnel or business practices in accordance with the organization's security goals. Technical controls (also known as logical controls) include hardware or software mechanisms used to protect assets. This includes things like fences, gates, guards, security badges and access cards, biometric access controls, security lighting, CCTVs, surveillance cameras, motion sensors, fire suppression, as well as environmental controls like HVAC and humidity controls.
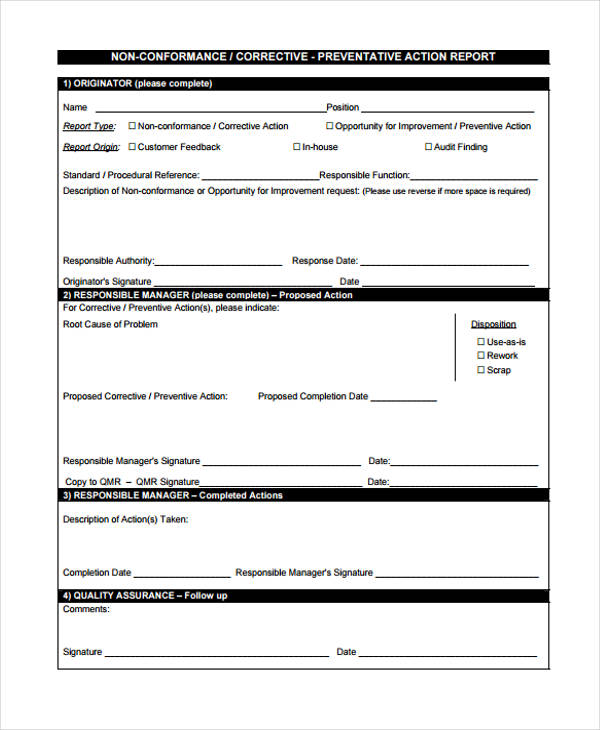
Physical controls describe anything tangible that’s used to prevent or detect unauthorized access to physical areas, systems, or assets.

One of the easiest and most straightforward models for classifying controls is by type: physical, technical, or administrative, and by function: preventative, detective, and corrective. Once an organization defines control objectives, it can assess the risk to individual assets and then choose the most appropriate security controls to put in place. “Our controls provide reasonable assurance that critical systems and infrastructure are available and fully functional as scheduled” is another example. For example, “Our controls provide reasonable assurance that physical and logical access to databases and data records is restricted to authorized users” is a control objective.

This is followed by defining specific control objectives-statements about how the organization plans to effectively manage risk. They typically flow out of an organization’s risk management process, which begins with defining the overall IT security strategy, then goals. Security controls are not chosen or implemented arbitrarily. Recognizable examples include firewalls, surveillance systems, and antivirus software. They include any type of policy, procedure, technique, method, solution, plan, action, or device designed to help accomplish that goal. Security controls exist to reduce or mitigate the risk to those assets. That generally includes people, property, and data-in other words, the organization’s assets. At the most fundamental level, IT security is about protecting things that are of value to an organization.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
